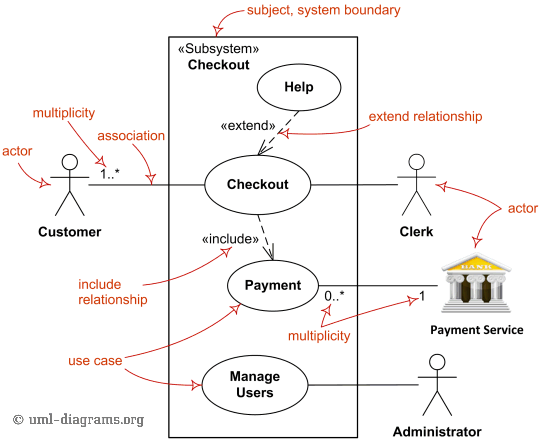
Use Case Diagram
A Use Case Diagram is a visual representation of the interactions between actors and a system. It is used to show the functionalities of a system from a user’s perspective, highlighting what the system does rather than how it does it.
Key Components
UML is the default tool for graphical representation. Specification Overview
Example Diagram
-
Actors:
- Represent entities (people, other systems) that interact with the system.
- Symbol: Stick figure.
-
Use Cases:
- Describe the actions or functions that the system provides.
- Symbol: Oval/ellipse with the name of the use case inside.
-
System Boundary:
- Represents the scope of the system.
- Symbol: A rectangle enclosing all the use cases.
-
Relationships:
- Associations:
- Represent interactions between actors and use cases.
- Symbol: A solid line connecting actors to use cases.
- Include:
- Indicates that a use case includes the behavior of another use case.
- Symbol: Dotted arrow pointing toward the included use case.
- Extend:
- Indicates that a use case may be extended by another use case under certain conditions.
- Symbol: Dotted arrow pointing toward the extending use case.
- Generalization:
- Represents an inheritance relationship between actors or use cases.
- Symbol: Solid line with a hollow arrowhead pointing toward the general actor or use case.
- Associations:
Heuristic Rules for Better Use Case Diagram Usability
(Hadi Putra & Hasibuan, 2018)
-
Arrange Use Cases by Expected Normal Sequence of Flow of Events
- The sequence of use cases should follow a logical flow from top-left to bottom-left within the system boundary.
-
Manage Use Case Diagram Complexity by Calibrating the Level of Abstraction
- Closely related use cases should be grouped to enhance overall readability and comprehension.
- For complex diagrams, the use case diagram should have no more than 10 use cases, all with proper levels of abstraction.
-
Use Actor Generalization to Indicate Level of Access
- Actor generalization helps identify access levels or roles, often a reflection of non-functional requirements.
-
Maintain Identical Dimensions for Use Case Ellipses and Appropriate White Spaces
- Ensure consistent dimensions for use case ellipses and maintain adequate white space between them for visual clarity.