Contention-Based Protocols
Overview
- Contention-based protocols operate on a first-come, first-served principle.
- They manage how workstations compete for access to the LAN medium.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
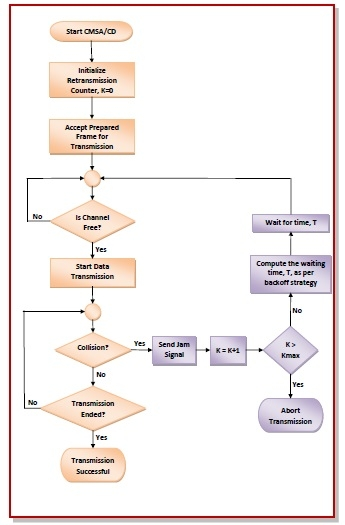
CSMA/CD Flowchart
- CSMA/CD is the most common example of a contention-based protocol.
- Operation:
- A workstation can transmit data if the medium is clear (i.e., no other workstation is transmitting).
- If the medium is busy, the workstation backs off and waits.
Collision Handling
- Collision: Occurs if two workstations transmit simultaneously.
- When a collision is detected:
- Both workstations stop transmitting immediately.
- Each workstation then backs off for a random amount of time before attempting to retransmit.
- The random backoff helps to prevent repeated collisions by ensuring that both workstations do not retransmit at exactly the same time.
Characteristics
- CSMA/CD is an example of a nondeterministic protocol, as it does not guarantee when a particular workstation will get access to the medium.