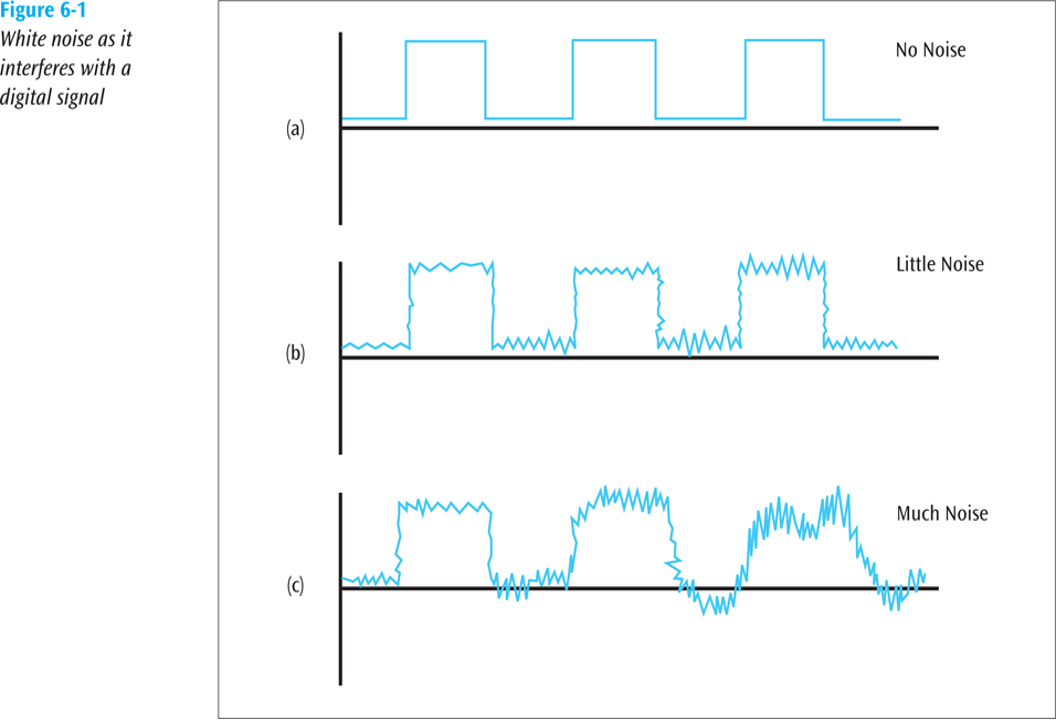
White Noise
White Noise is a type of noise commonly encountered in communication systems, known for its broad frequency spectrum and relatively constant power across all frequencies. Here’s an overview:
White noise
Characteristics
- Also Known As: Thermal noise or Gaussian noise.
- Frequency Spectrum: White noise has a uniform distribution of power across all frequencies, which means it affects all frequencies equally.
- Power: The power of white noise is relatively constant across the spectrum, leading to a consistent level of noise interference.
Impact on Communication Systems
- Disruption: If the level of white noise becomes too strong, it can severely disrupt the signal, making it difficult or impossible to accurately receive or decode the transmitted information.
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): White noise can lower the signal-to-noise ratio, which is a measure of signal quality relative to the noise level. A lower SNR indicates higher noise levels compared to the signal.
Management and Reduction
- Shielding and Filtering: Techniques such as shielding cables and using filters can help reduce the impact of white noise.
- Signal Processing: Advanced signal processing algorithms can be employed to mitigate the effects of white noise and improve signal clarity.
Summary
- White Noise: Known as thermal or Gaussian noise, it has a constant power across all frequencies.
- Impact: Can disrupt signals if too strong, reducing signal quality and increasing the difficulty of accurate data transmission.
- Management: Techniques like shielding, filtering, and signal processing can help reduce the impact of white noise.
Managing white noise is essential for maintaining the quality and reliability of communication systems, particularly in environments where noise levels can significantly affect signal integrity.