Fiber-Optic Cable
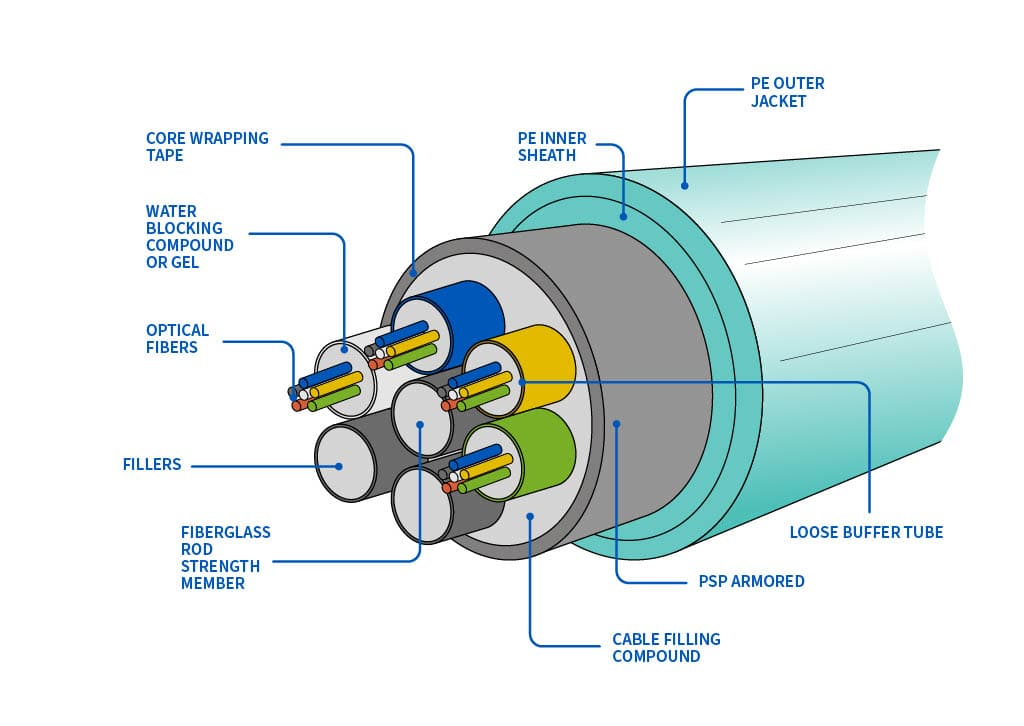
What is it?
-
Structure: A thin glass cable (slightly thicker than a human hair) surrounded by a plastic coating, packaged into an insulated cable.
-
Function:
- A photo diode or laser generates pulses of light that travel down the fiber optic cable.
- These pulses are received by a photo receptor.
Why is it used?
-
Advantages:
- Highest data rate: Capable of carrying the highest data rates over the longest distances.
- Security: Not affected by electromagnetic noise and cannot be easily wiretapped.
- Cost: While the initial cost is higher than twisted pair cables, it’s lower than coaxial, and its superior performance outweighs the cost.
-
Disadvantages:
- Requires two fibers for a round-trip connection.
- Still vulnerable to noise, despite being immune to electromagnetic interference.