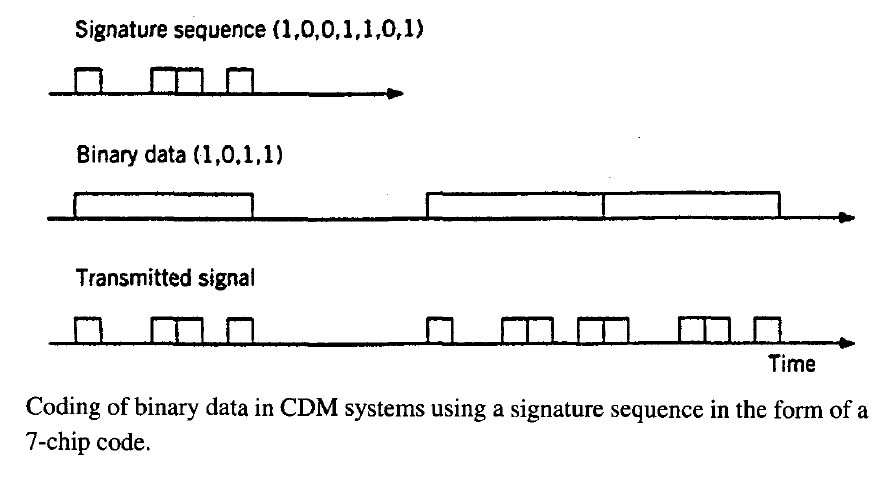
Code Division Multiplexing
Code Division Multiplexing (CDM), also known as Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), is an advanced multiplexing technique that allows multiple devices to transmit on the same frequencies simultaneously. Here’s a detailed overview:
Basic Principles
- Unique 64-bit Code: Each mobile device is assigned a unique 64-bit code.
- To send a binary 1, the device transmits its unique code.
- To send a binary 0, the device transmits the inverse of the code.
- To send nothing, the device transmits all zeros.
Signal Reception and Decoding
- Receiver Process:
- The receiver gets the summed signal and multiplies it by the receiver’s code.
- It adds up the resulting values:
- Interprets as a binary 1 if the sum is near +64.
- Interprets as a binary 0 if the sum is near -64.
CMDA
Example with 8-bit Code
-
Mobile Devices and Their Codes:
- Mobile A:
11110000 - Mobile B:
10101010 - Mobile C:
00110011
- Mobile A:
-
Transmission:
- Mobile A sends a 1 (code:
11110000, or++++----). - Mobile B sends a 0 (code:
01010101, or-+-+-+-+). - Mobile C sends a 1 (code:
00110011, or--++--++).
- Mobile A sends a 1 (code:
-
Received Signal:
- Summed signal:
-1, +1, +1, +3, -3, -1, -1, +1
- Summed signal:
-
Decoding for Mobile A:
- Mobile A’s code:
+1, +1, +1, +1, -1, -1, -1, -1 - Product result:
-1, +1, +1, +3, +3, +1, +1, -1 - Sum of Products:
+8 - Binary 1: Result near +8.
- Mobile A’s code:
-
Decoding for Mobile B:
- Mobile B’s code:
+1, -1, +1, -1, +1, -1, +1, -1 - Product result:
-1, -1, +1, -3, -3, +1, -1, -1 - Sum of Products:
-8 - Binary 0: Result near -8.
- Mobile B’s code:
CDMA Applications
-
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems): CDMA is used in UMTS, also known as W-CDMA.
-
Advantages:
- Provides better signal-to-noise ratio compared to conventional TDMA and FDMA.
- Allows for variable user capacity as long as the total energy of the multiuser signal remains constant.
-
Disadvantages:
- Power control issues limit the maximum number of users in a cell.
-
Alternatives for CDMA in UMTS:
- W-CDMA
- TD-CDMA
- FD-CDMA