Blockchain
What is Blockchain?
Ledger illustration
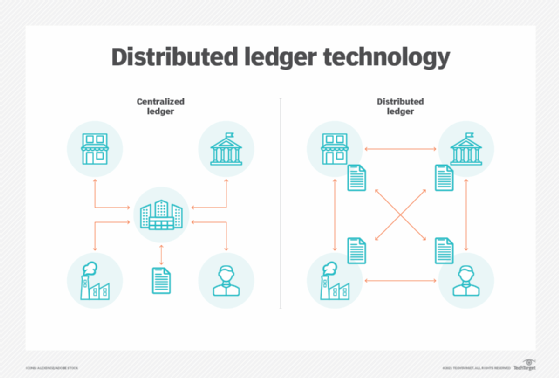
- Blockchain is a shared ledger technology that allows any participant in a business network to access a system of record (ledger).
- Blockchain Key Characteristics
- Fundamentally, a blockchain is an immutable, distributed ledger.
Key Features
- Blockchain is a mathematical framework designed to securely store data, making it highly tamper-resistant. Transactions are handled by Validating and Mining Transactions
- It is suitable for securely tracking a wide range of information such as:
- Account & trade balances
- Ownership of property
- Taxes
- Births, deaths, marriages
- Charges, transactions, property sales
Economic Infrastructure
- Blockchain is a new economic infrastructure that maintains records.
- Using blockchain, participants can exchange value easily, just like sending a text message, without relying on a central authority to verify transactions.
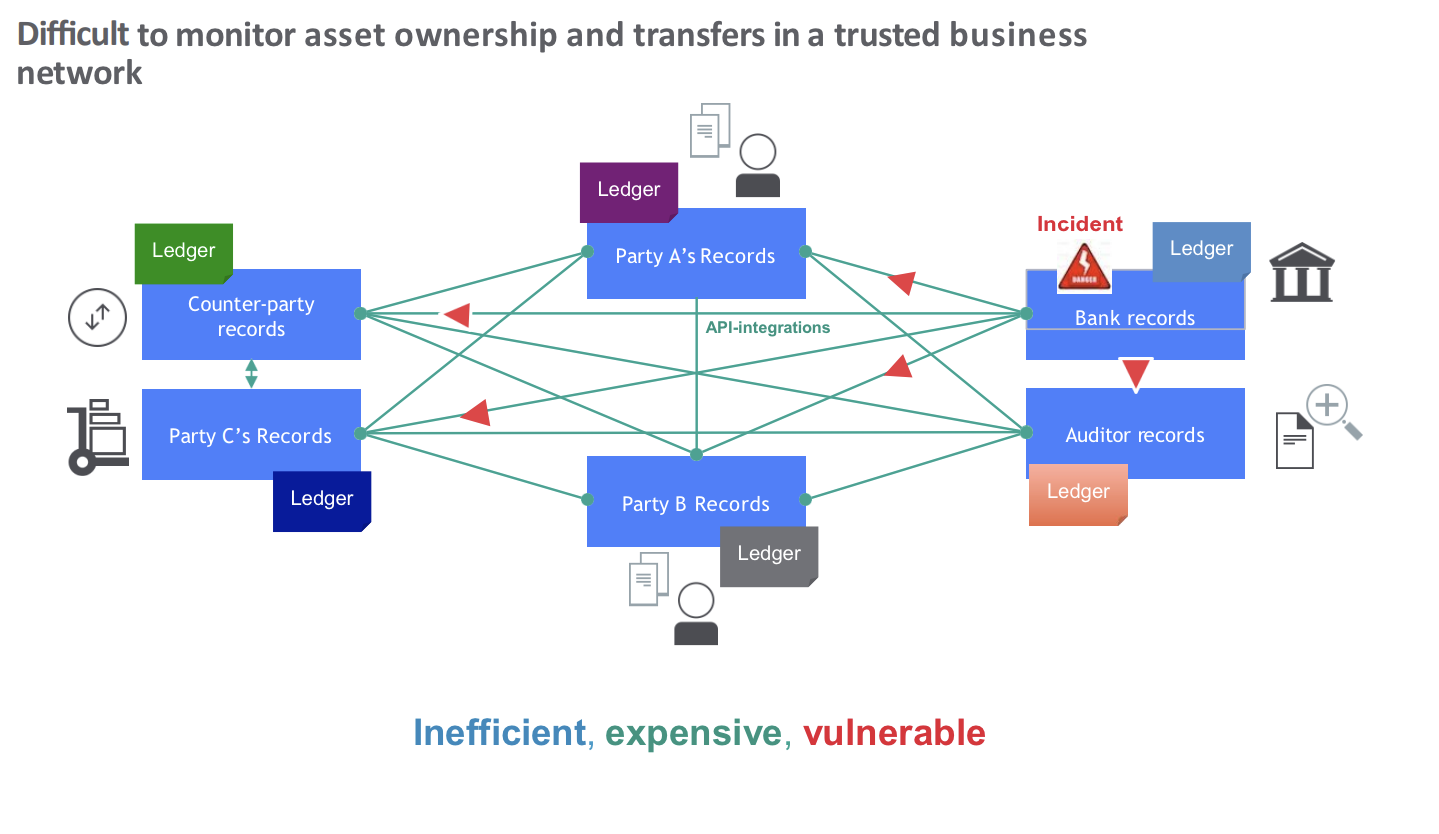
Problem
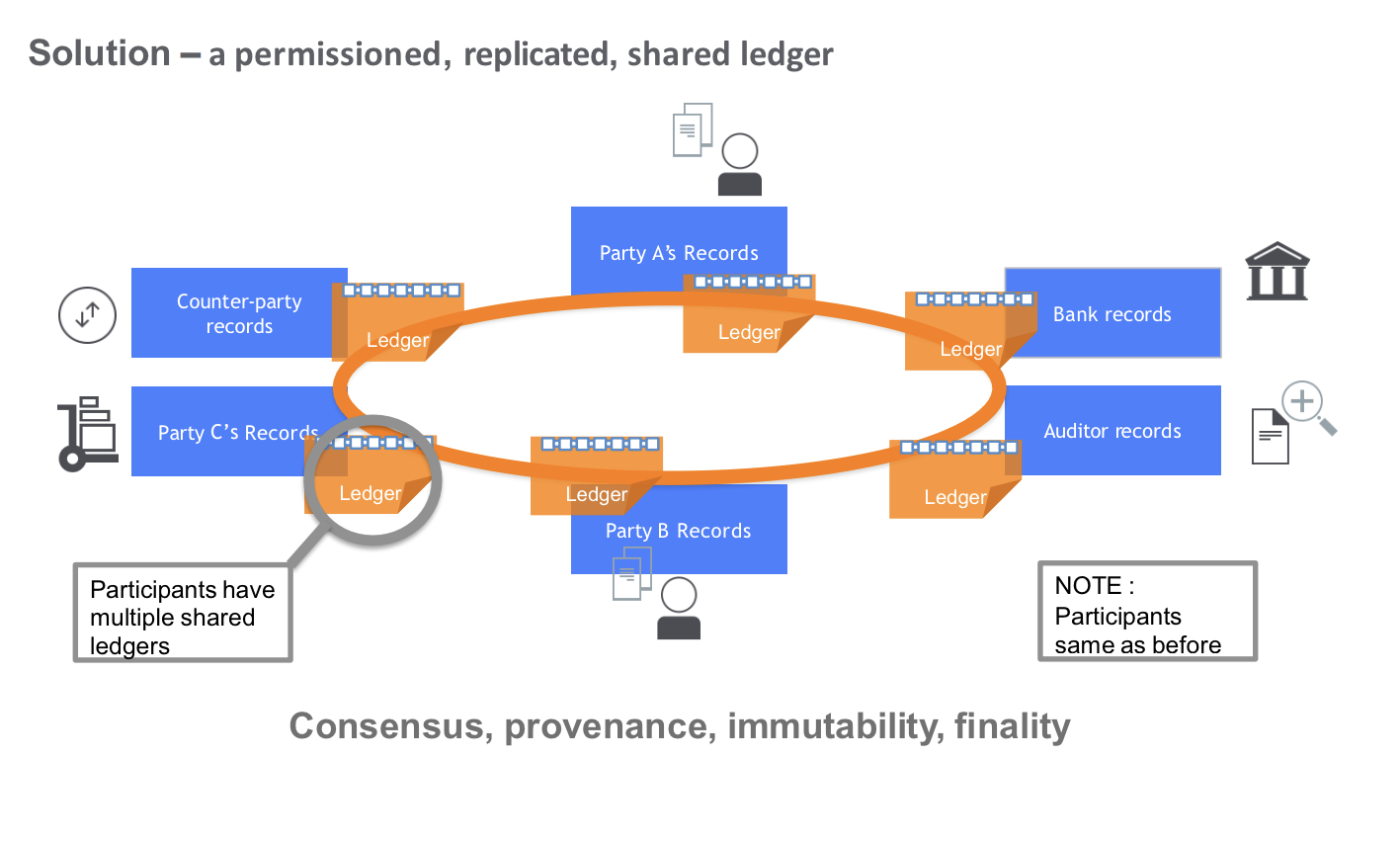
Solution
Initial Application: Bitcoin
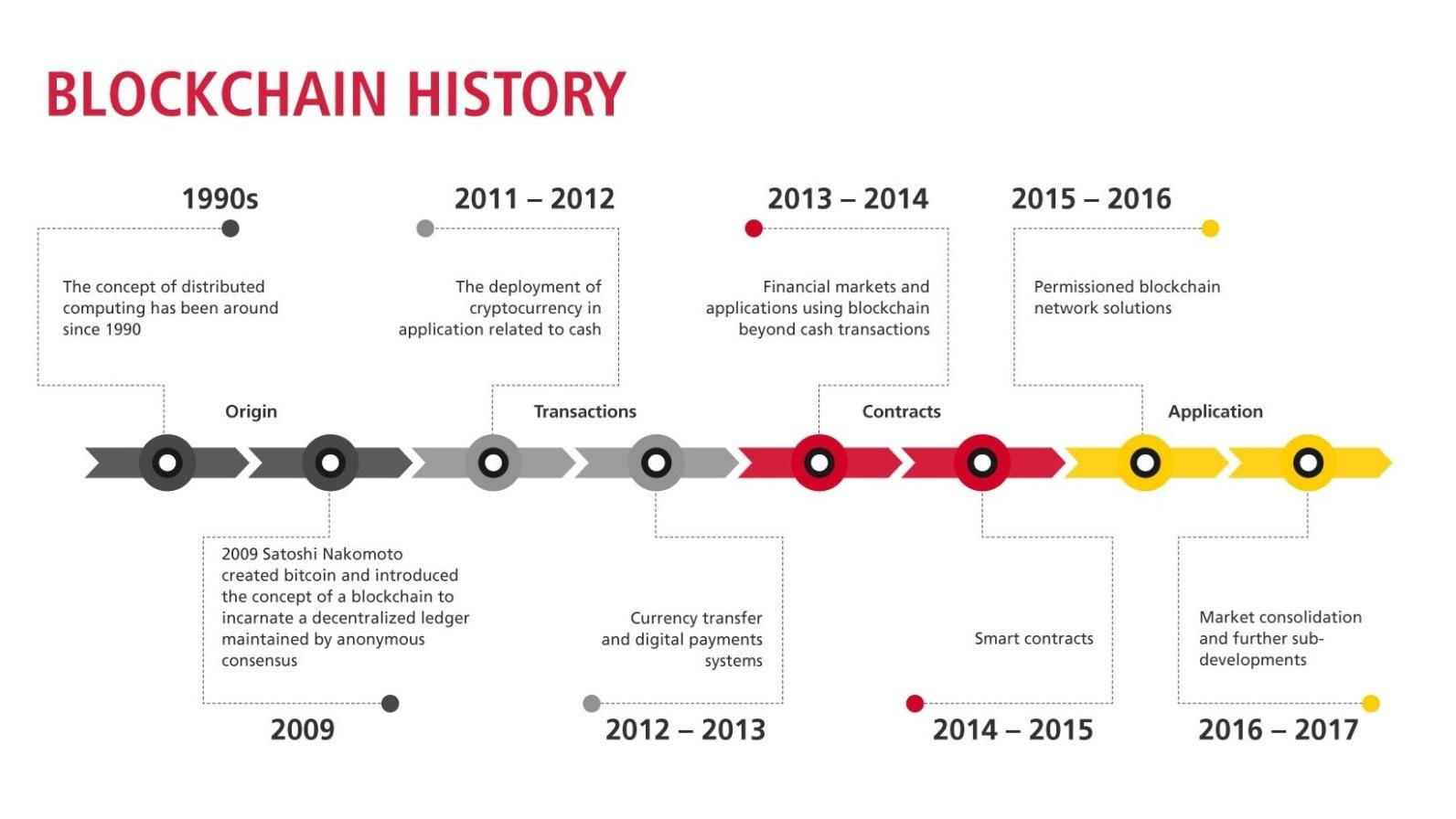
Blockchain Milestones
- The first use of blockchain was with Bitcoin, where each node on the network keeps a duplicate of the ledger.
- Miners solve cryptographic puzzles to create a universally accepted record of transactions.
Trust and Traceability
- Blockchain promotes automated trust, securely sharing sensitive data and providing visibility into who has accessed or modified it.
- This ensures full traceability of transactions and records.
Contract Management
- Smart contracts on the blockchain automate record-keeping and sharing.
- They eliminate the need for:
- Manual contracts
- Invoice reconciliation
- Manual signatures
Data Sharing
- Blockchain ensures that stored information is immutable and resistant to tampering.
- It enables the use of:
- Digital certificates
- Digital signatures
- Tracing the history of a product before purchase