Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
- Broad Frequency Range: UWB broadcasts over a wide range of frequencies simultaneously, not limited to a fixed bandwidth.
- Low Power: Uses very low power levels, minimizing the risk of interference with other sources operating on the same frequencies.
- Speeds: Can achieve speeds up to 100 Mbps, typically for short distances such as in wireless LANs.
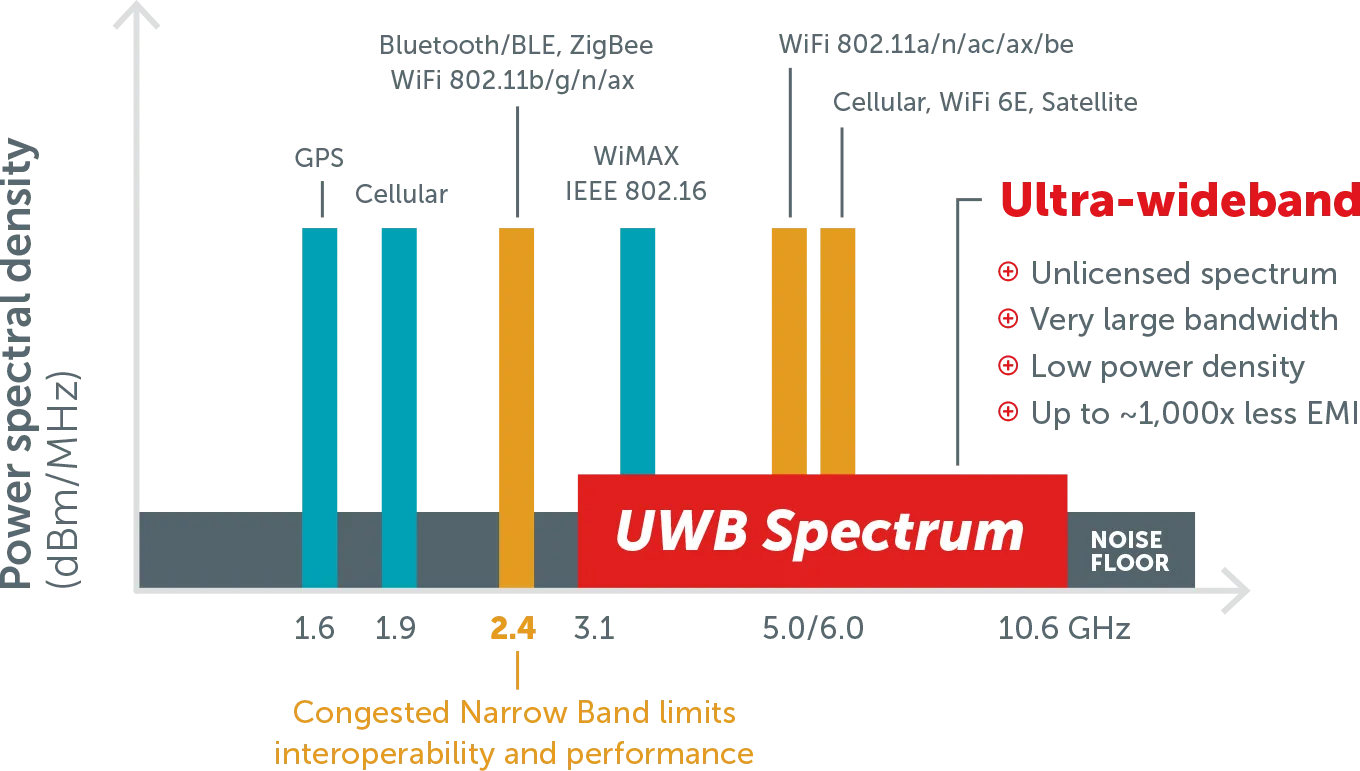
Advantages and Disadvantages
-
Proponents’ View:
- UWB is seen as beneficial for sharing frequencies with other sources without causing significant interference.
- Claims of “getting something for nothing” due to efficient use of shared frequencies.
-
Opponents’ Concerns:
- Cell Phone Industry: Concerns about UWB’s interference with CDMA technology, which is sensitive to such interference.
- GPS: Potential for UWB to affect GPS signals.
-
Potential Solutions:
- Dual Systems: Implementing two types of UWB systems:
- Indoor: Higher power levels.
- Outdoor: Reduced power (about 1/10 of indoor power) to minimize interference.
- Dual Systems: Implementing two types of UWB systems: