Wireless Local Area Networks (IEEE 802.11)
- Transmits data between workstations and local area networks using high-speed radio frequencies.
- Current technologies support up to 1000 Mbps (theoretical) data transfer at distances up to hundreds of feet.
- Popular standards include IEEE 802.11b, a, g, n, ac, and ax.
Wi-Fi Standards
-
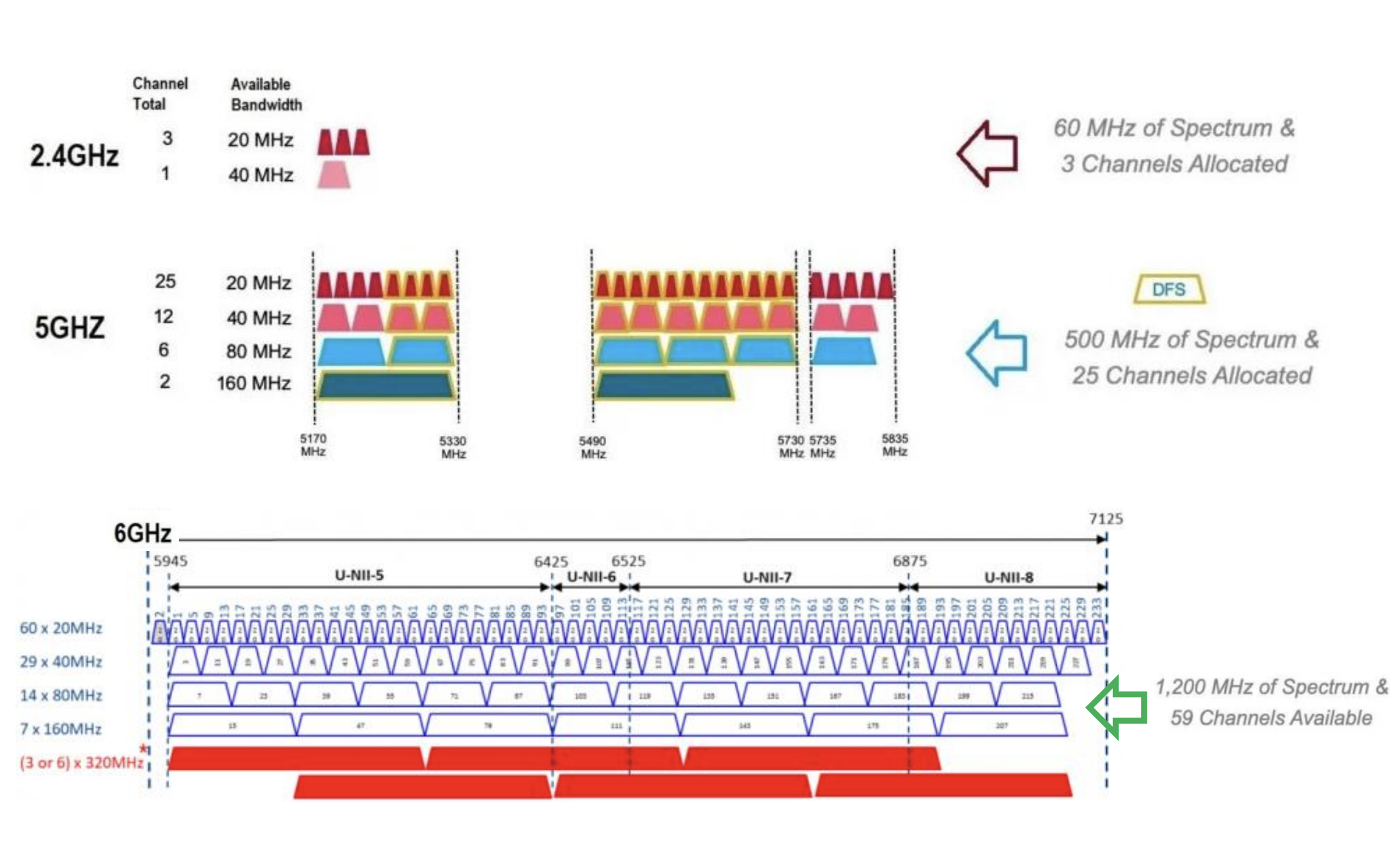
Wi-Fi 1: IEEE 802.11b
- 11 Mbps
- 2.4 GHz
- 20 MHz
-
Wi-Fi 2: IEEE 802.11a
- 54 Mbps
- 5 GHz
- 20 MHz
-
Wi-Fi 3: IEEE 802.11g
- 54 Mbps
- 2.4 GHz
- 20 MHz
-
Wi-Fi 4: IEEE 802.11n
- Up to 600 Mbps
- 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- 20 MHz, 40 MHz
-
Wi-Fi 5: IEEE 802.11ac
- Up to 1 Gbps (theoretical)
- 5 GHz
- 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz
-
Wi-Fi 6: IEEE 802.11ax
- Up to 9.6 Gbps (theoretical)
- 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz (with potential for future 6 GHz)
- 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz
- Improved efficiency, capacity, and performance in dense environments.
Spectrum Band