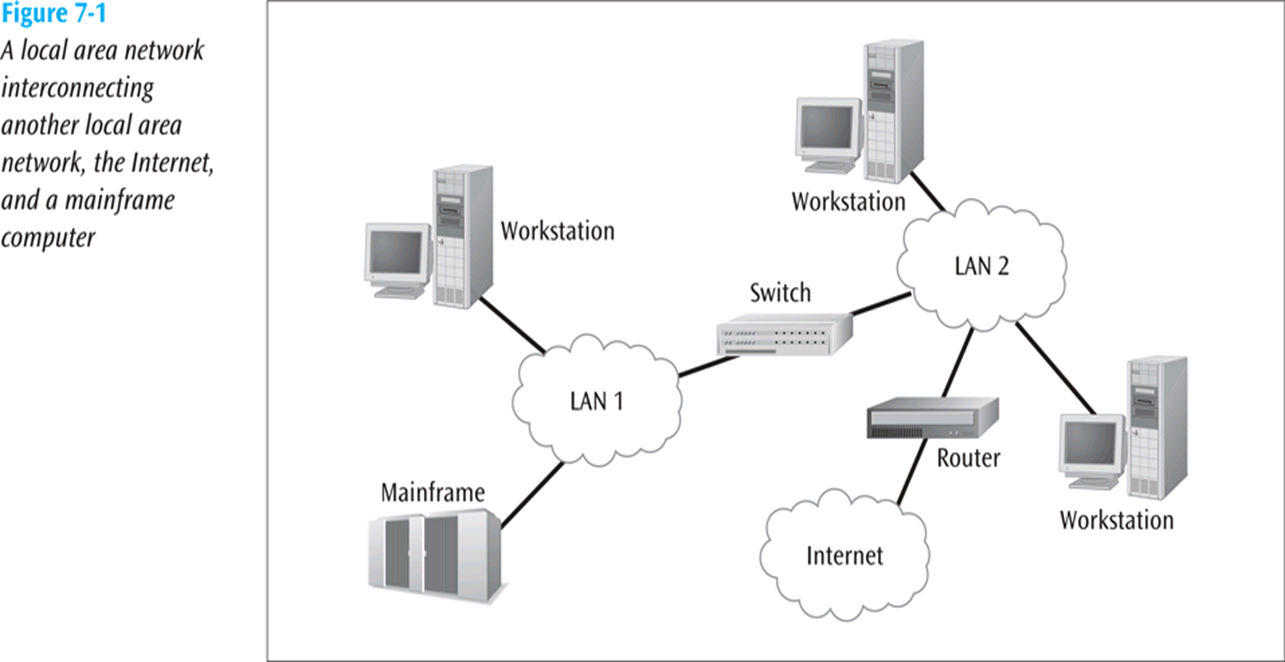
Local Area Network (LAN)
Local Area Networks (LANs) are critical for facilitating communication and resource sharing within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or campus. Below are key concepts associated with LANs:
Local Area Network
Network Protocols
-
Contention-Based Protocols: These protocols manage access to the shared communication medium in a network where multiple devices compete to send data. Devices “contend” for the medium, which can lead to collisions.
-
Medium Access Control Protocols: Protocols that determine how devices on a network gain access to the communication medium. These protocols are essential for managing data transmission and preventing collisions.
-
Round-Robin Protocol: A scheduling method used in contention-based environments to provide fair access to the communication medium. Each device is given a turn in a cyclic order to send data.
Addressing
-
IP Addresses and Subnetting: IP addresses uniquely identify devices on a network, while subnetting divides a network into smaller, manageable segments. This helps in optimizing network performance and improving security.
-
IPv4: The fourth version of the Internet Protocol, using 32-bit addresses to identify devices on a network. IPv4 is the most widely used version but is gradually being replaced by IPv6 due to address space limitations.
-
IPv6: The sixth version of the Internet Protocol, utilizing 128-bit addresses to accommodate the growing number of devices connected to the Internet. IPv6 addresses the limitations of IPv4 and provides improved routing and security features.
-
MAC Addresses: Media Access Control addresses are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications at the data link layer. MAC addresses are essential for local network operations.
Network Issues
-
Exposed Terminal Problem: A scenario in wireless networks where a device is unable to send data because it cannot detect ongoing transmissions from other devices within range, even though it would not cause a collision.
-
Hidden Terminal Problem: A situation where two devices cannot detect each other’s transmissions due to distance or obstacles, potentially leading to collisions at the receiving device.
LAN Technologies
-
Wired Ethernet: A widely used LAN technology that connects devices using Ethernet cables. Wired Ethernet is known for its reliability and high data transfer rates.
-
Wireless Ethernet: A LAN technology that connects devices wirelessly, typically using Wi-Fi standards. Wireless Ethernet provides mobility and ease of installation.
-
Power over Ethernet (PoE): A technology that allows network cables to carry electrical power along with data, simplifying installation by reducing the need for additional power outlets for devices like IP cameras and VoIP phones.
Network Components
-
Switch: A network device that connects multiple devices within a LAN, using MAC addresses to forward data to the correct destination. Switches improve network efficiency by reducing collisions.
-
Full-Duplex Switches: Switches that allow simultaneous data transmission and reception, enhancing network performance by enabling devices to communicate without waiting for the medium to become available.
-
Star-Wired Bus: A network topology where devices are connected to a central hub or switch, forming a star shape. This topology is commonly used in modern LAN designs.
Network Design and Traffic Management
-
LAN Topology: The physical and logical arrangement of devices in a LAN. Common topologies include star, bus, and ring configurations, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
-
Isolating Traffic Patterns and Providing Multiple Access: Techniques used in LANs to manage data flow and ensure that multiple devices can communicate without interference. Virtual LANs (VLANs) are often employed for traffic isolation.
-
Virtual LANs: A logical subdivision of a LAN that allows devices to be grouped together regardless of their physical location. VLANs enhance security and improve network management.
-
Wireless CSMA CA: Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance is a protocol used in wireless networks to prevent data collisions. It allows devices to sense the medium before transmitting and uses techniques to avoid collisions.
-
WLAN Frequency Planning: The process of planning and managing the frequency spectrum used by wireless LANs to minimize interference and optimize performance.
Understanding these concepts is essential for effectively designing, implementing, and managing Local Area Networks to meet the communication needs of users and devices within a specific area.