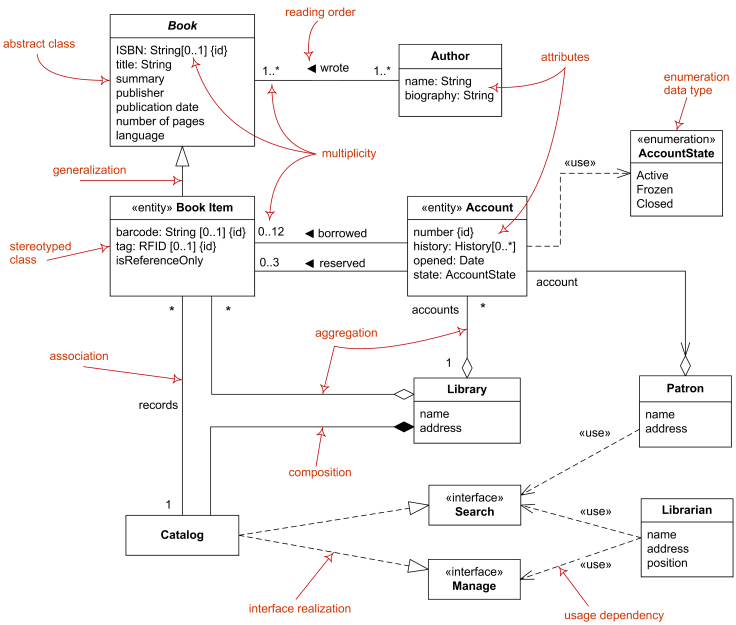
Class Diagrams
Overview
- Definition: A static model that shows classes and their relationships to one another.
Example Class Diagram
Elements
- Classes:
- Objects within the system (e.g., person, place, thing).
- Stores and manages information and contains:
- Attributes: Characteristics of the class.
- Operations: Activities the class can perform.
- Relationships:
- Associations between classes, depicted as lines.
- Multiplicity indicates how many of one object is associated with another.
Attributes
- Definition: Properties of a class.
- Examples: Last name, first name, address, etc.
- Derived Attributes:
- Preceded with a slash (/), e.g., age derived from date of birth.
- Visibility:
- Public (+): Visible to all classes.
- Private (-): Visible only to the class instance in which they are defined.
- Protected (#): Visible to the class instance and its descendants.
Operations
- Common operations are not shown (create/delete, return/set value).
- Types of Operations:
- Constructor: Creates an object.
- Query: Provides information about the object’s state.
- Update: Changes values of some or all attributes.
- Destructor: Deletes or removes an object.
Relationships
- Denotes associations between classes.
- Depicted with a line labeled with the name of the relationship.
- Directional Relationships: Depicted with a triangle (e.g., a patient schedules an appointment).
- Self-Associations: Classes related to themselves (e.g., employees and managers in the same class).
Multiplicities
- Department Boss: 1 to 1 (A department has one and only one boss).
- Employee Child: 1 to 0..* (An employee has zero to many children).
- Boss Employee: 1 to 1..* (A boss is responsible for one or more employees).
Association Classes
- Common in many-to-many relationships.
- Used to record attributes about the relationship between two classes.
- Example: Students related to courses; a Grade class provides attributes describing this relationship.
Generalization & Aggregation
- Generalization:
- Denotes inheritance; properties and operations of the superclass are valid for the subclass.
- Depicted as a solid line with a hollow arrow pointing at the superclass.
- Aggregation:
- Denotes a logical “a-part-of” relationship.
- Composition:
- Denotes a physical “a-part-of” relationship.
Simplifying Class Diagrams
- Fully populated class diagrams can be difficult to understand.
- Common simplifications:
- Show only concrete classes.
- The view mechanism shows a subset of classes.
- Packages show aggregations of classes or any elements in UML.