Validating and Mining Transactions
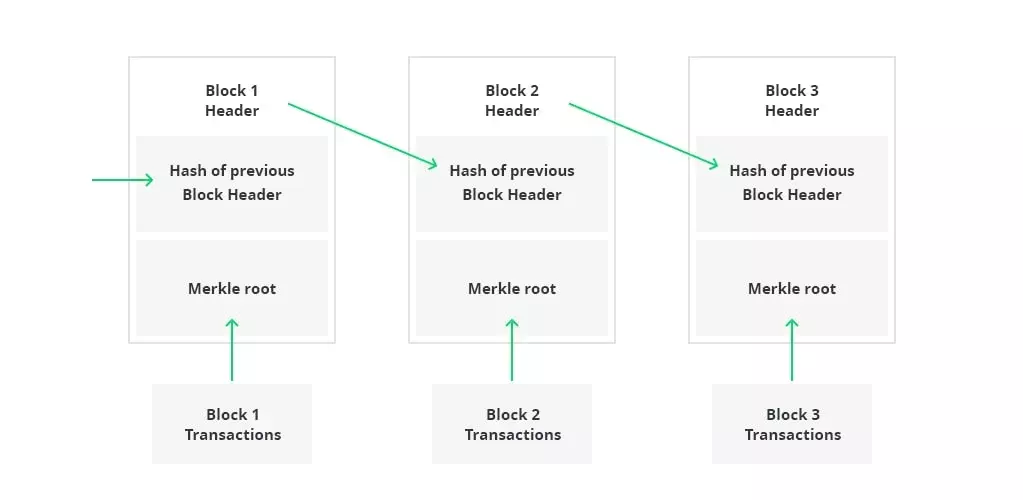
Blockchain ledger structure
Validating Transactions
- Users must affix a digital signature using a cryptographic key to validate a transaction before submitting it.
- Once submitted, each node verifies the transaction to ensure:
- Feasibility
- Proper authentication
- If the transaction fails verification, it is rejected.
- If more than half of the nodes agree on the validity, the transaction is deemed legitimate and enters a queue.
Mining Transactions
- A mining node validates a set of queued transactions, grouping them into a block.
- The mining node then publishes the block across the network and adds it to the blockchain.
- Invalid transactions discovered during this process are discarded.
Impact of Transaction Modifications
- Any modification to a transaction will entirely change its hash code, affecting the block and all connected blocks.
- This creates a cascading effect across the blockchain.
- Nodes will detect the change and reject the modified transaction.