Cellular Telephones
- Wireless telephone service: Also called mobile telephone, cell phone, and PCS (personal communications service)
- To support multiple users in a metropolitan area, the market is divided into cells, each with its own transmission tower and set of assignable channels.
1st Generation
- AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service): First popular cell phone service; used analog signals and dynamically assigned channels.
- D-AMPS (Digital AMPS): Applied digital multiplexing techniques on top of AMPS analog channels.
2nd Generation
- PCS (Personal Communication Systems): Essentially all-digital cell phone service.
- PCS phones came in three technologies:
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)
- GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
2.5 Generation
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service): Used by AT&T Wireless, Cingular Wireless, and T-Mobile in GSM networks (transmits data at 30 kbps to 40 kbps).
- CDMA2000 1xRTT: Used by Verizon Wireless, Alltel, U.S. Cellular, and Sprint PCS (transmits data at 50 kbps to 75 kbps).
- IDEN (Integrated Digital Enhanced Network): Used by Nextel (Sprint, ptt phone).
3rd Generation
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System): Also called Wideband CDMA; the 3G version of GPRS; not backward compatible with GSM.
- 1XEV (1 x Enhanced Version): 3G replacement for 1xRTT, with two forms:
- 1xEV-DO: For data only.
- 1xEV-DV: For data and voice.
4th Generation
- LTE (Long Term Evolution): Theoretical speeds of 100 Mbps or more; actual download speeds 10-15 Mbps (e.g., Verizon).
- WiMax: Theoretical speeds of 128 Mbps; actual download speeds 4 Mbps (e.g., Sprint and Clearwire).
- HSPA (High Speed Packet Access): 14 Mbps downlink, 5.8 Mbps uplink; debated as 3.5G or 4G.
- HSPA+: Theoretical downlink of 84 Mbps, uplink of 22 Mbps (e.g., T-Mobile); debated as 3.5G or 4G.
One of the candidate for 4G is WiMax
5th Generation
- 5G Technology: Will provide all possible applications using a universal device, interconnecting existing communication infrastructures.
- Reconfigurable multimode and cognitive radio-enabled terminals
- Software-defined radio modulation schemes: Reconfigurable software downloadable from the Internet.
- Development focus: User terminals will access multiple wireless technologies simultaneously and combine different flows.
- Core: Re-configurable, Multi-Technology Core, potentially integrating nanotechnology, cloud computing, cognitive radio, and artificial intelligence on an All IP Platform.
4G vs 5G
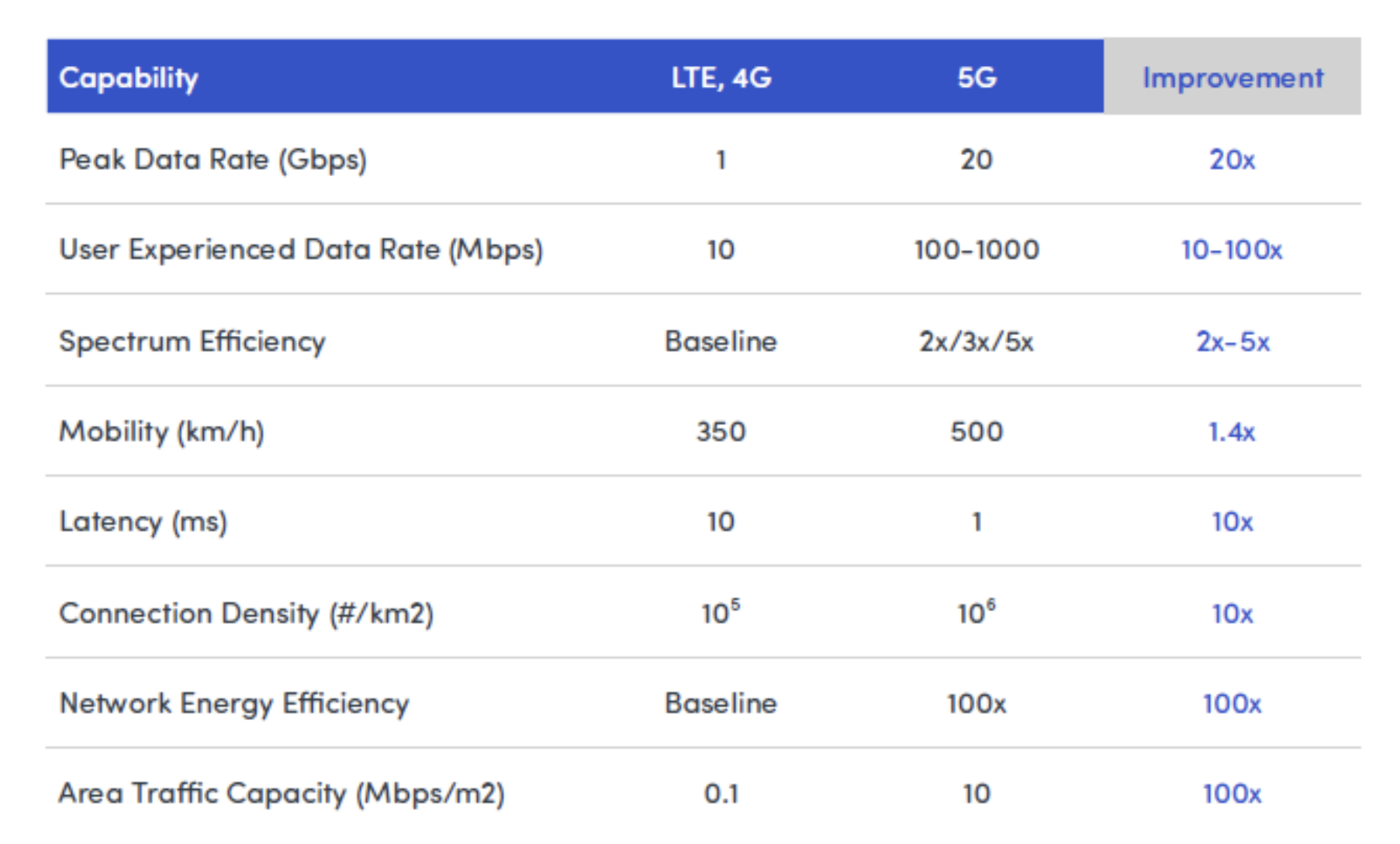
4G LTE
- Mobile Broadband: Provides high-speed internet access for mobile devices.
- Machine Type Communication: Supports communication between machines and devices.
5G NR (New Radio)
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: Improved data speeds and capacity for mobile internet.
- Massive Machine Type Communication: Handles a large number of devices and sensors communicating simultaneously.
- Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communication: Ensures very reliable connections with minimal delay, suitable for applications requiring high precision and speed.