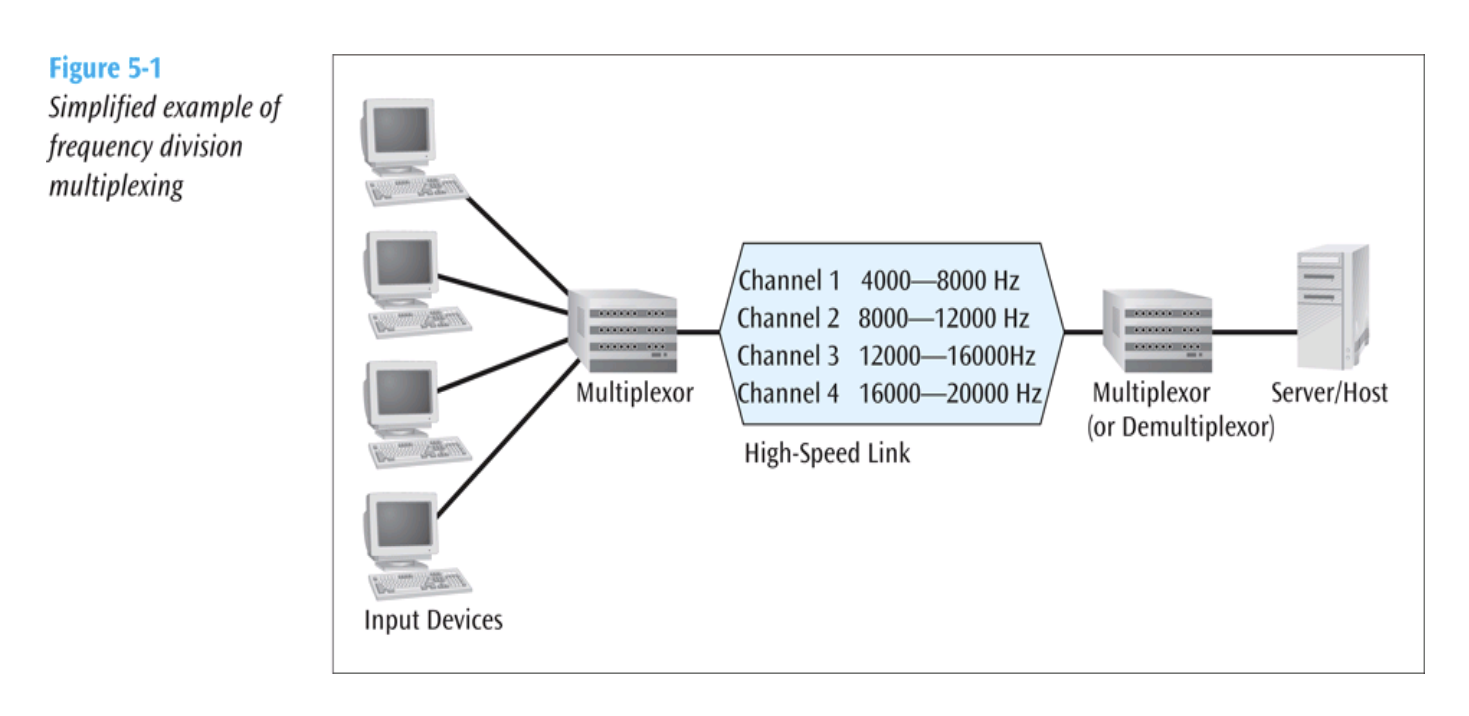
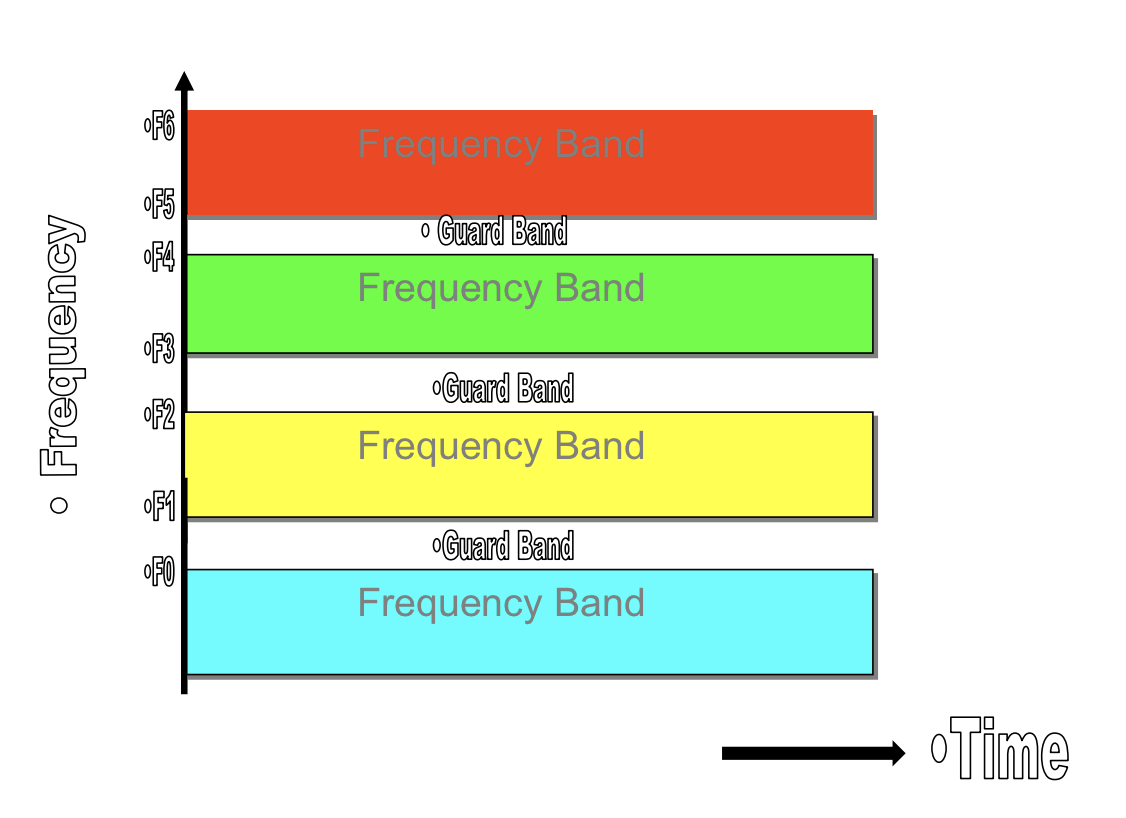
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Can also be called Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
- Assigns non-overlapping frequency ranges to each “user” or signal on a medium.
- All signals are transmitted at the same time but use different frequencies.
- A multiplexor assigns frequencies to each device and is connected to a high-speed communications line.
- A de-multiplexor separates the signals at the receiving end.
Frequency Division
Demultiplexing
- Performed via band pass filter (BPF) at the receiver.
- Low pass filter (LPF) produces the original signal.
Analog Signaling
- Used in older systems; more recent systems use discrete analog signals.
- Broadcast radio, television, cable TV, and cellular systems utilize FDM.
- It is the oldest multiplexing technique and may be susceptible to noise due to analog signaling.
FDM Illustration
FDMA Applications
- Used in telephone systems, radio systems, and cable TV.
- Utilized in the first generation of mobile networks (FD and TDMA).
- GSM uses FDMA with TDMA.
- UMTS (3G) combines FDMA with other multiplexing techniques.