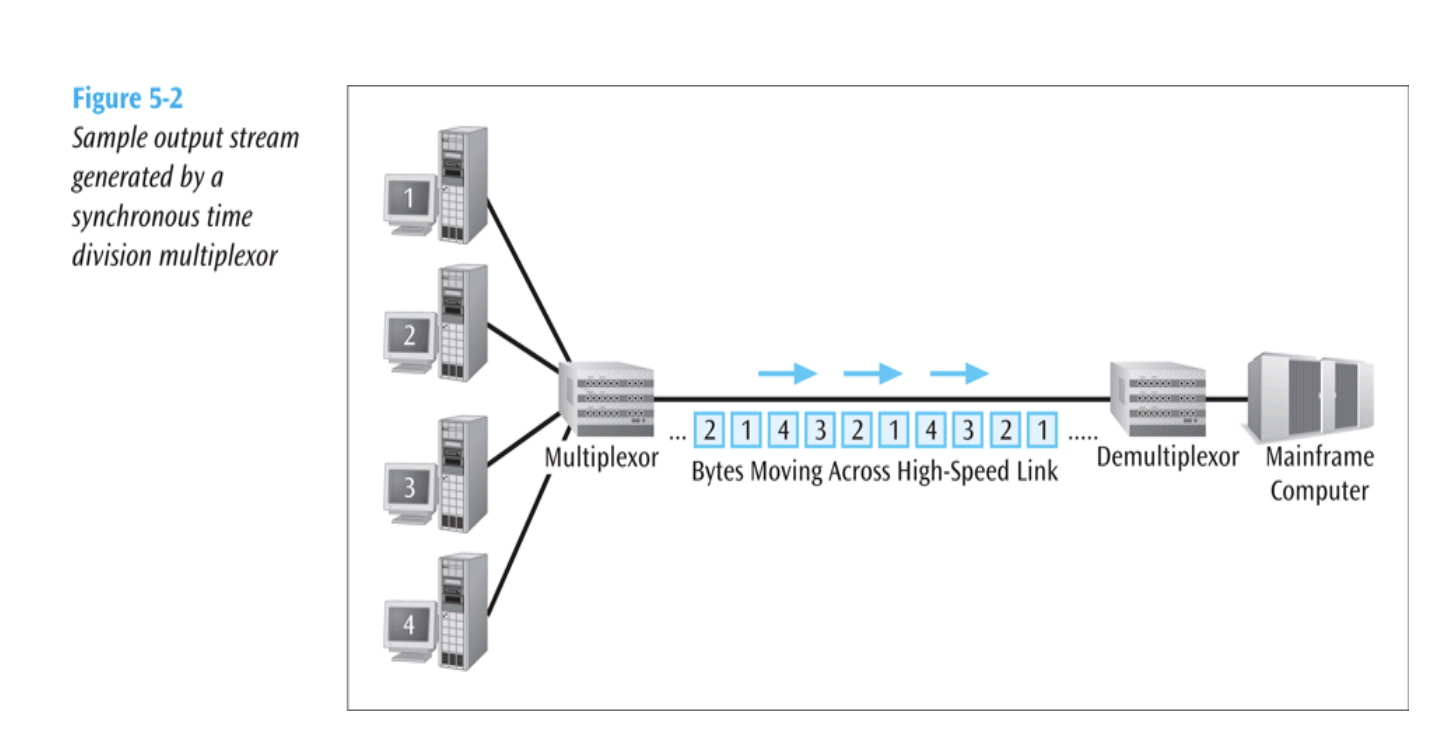
Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing (STDM)
- The original form of time division multiplexing.
- The multiplexor accepts input from devices in a round-robin fashion and transmits data in a continuous pattern.
- Common examples: T-1 and SONET telephone systems.
STDM Illustration
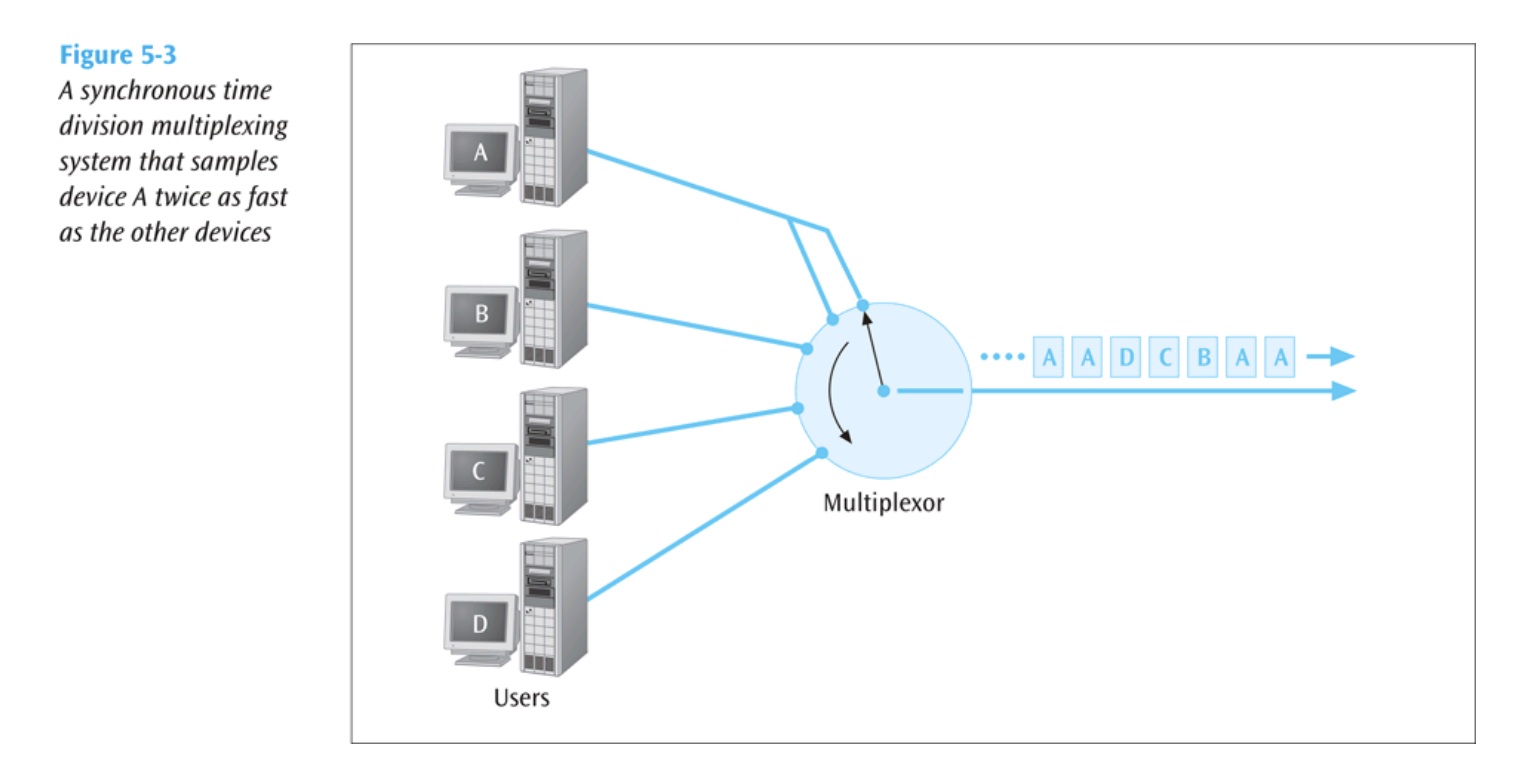
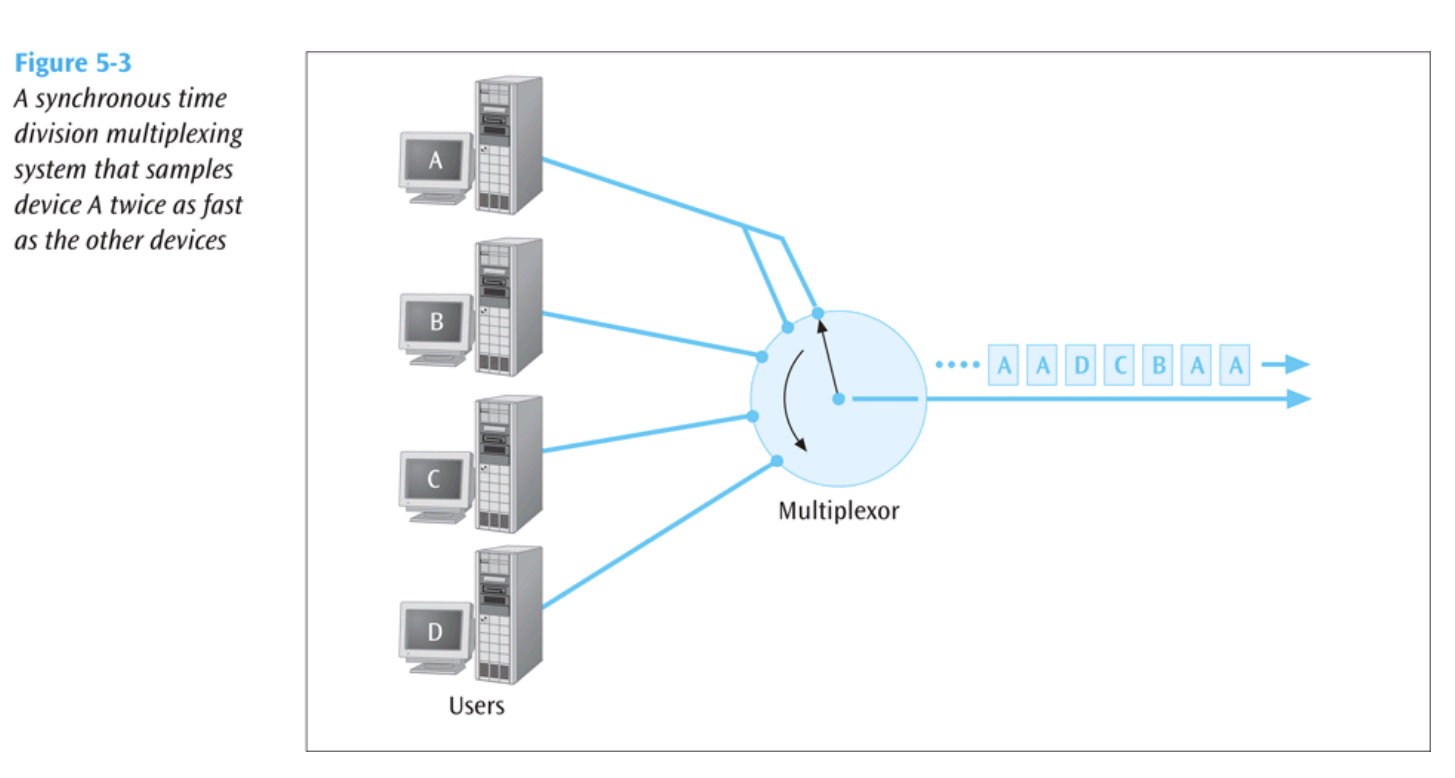
Handling Different Data Rates
- If a device generates data at a faster rate, the multiplexor must either:
- Sample the faster data stream more frequently.
- Buffer the faster data stream.
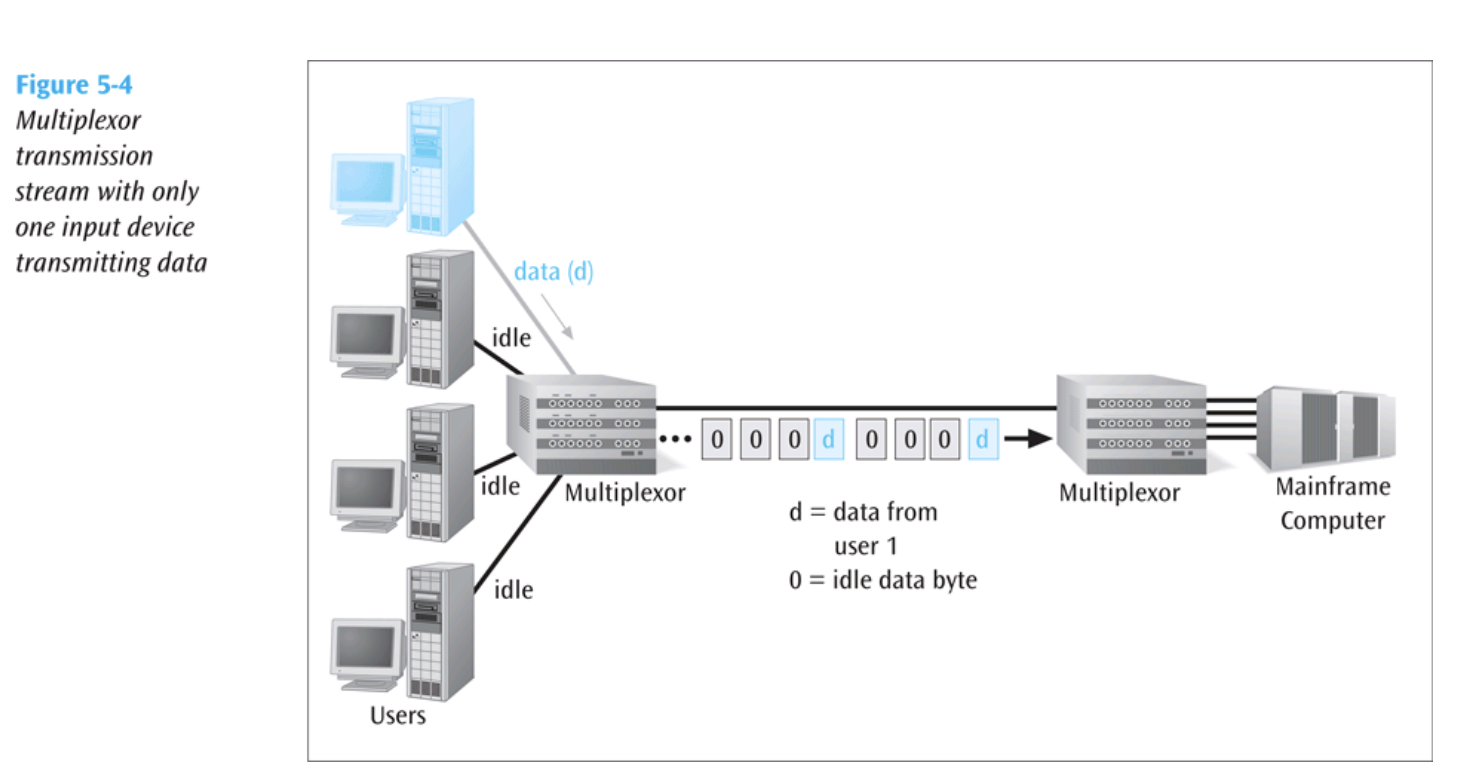
- If a device has nothing to transmit, the multiplexor inserts a placeholder into the stream.
Native Implementation
Bandwidth is allocated equally
May waste resource sending data for inactive terminals
Multiplexor
Bandwidth is allocated by multiplexor
Synchronization
- To keep the receiver synchronized with the data stream, the transmitting multiplexor may insert alternating 1s and 0s into the data stream.